7/7 Overall, we provided several lines of evidence that transh contacts may play a role in the fruit fly embryonic development through regulation of chromatin activity.
Assistant Professor, University of Warsaw. #bioinformatics #computerscience #genomics #rstats #machinelearning
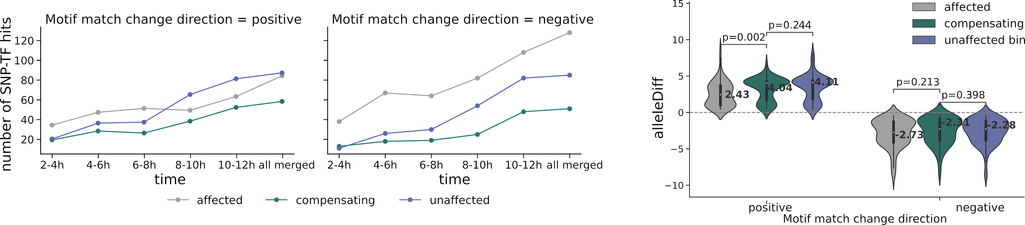
6/7 We also used motifbreakR to assess the impact of haplotype-specific variants on putative TF binding sites at transh-up triads. These binding sites are defined by TF motif instances at DNase-seq peaks from a range of developmental time windows.
The affected haplotypes have the most SNV-TF hits yelding worse motif match, while the compensating haplotypes the least. However, at individual variants the difference in effect size is significant only for hits with positive change in motif score.
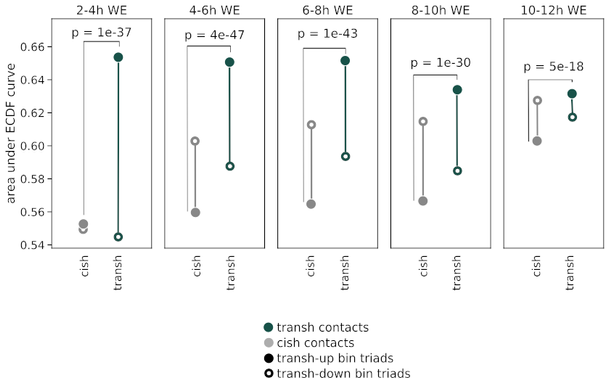
5/7 We checked the distance between individual chromatin contacts and closest open chromatin peaks at different stages of embryonic development. The transh contacts from transh-up triads are significantly closer to open chromatin, esp. at 2-4h.
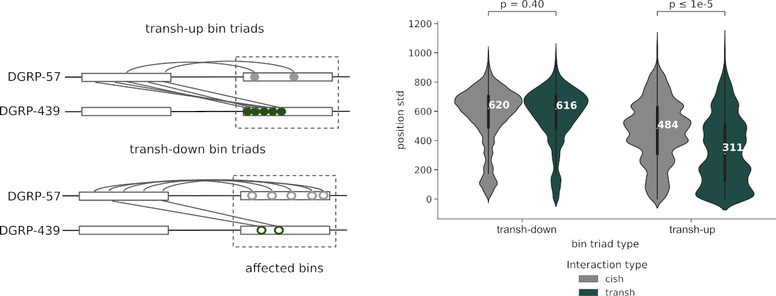
4/7 We found that individual transh contacts in transh-up bin triads are tightly clustered within the genomic bins, compared to cish interactions at the affected bins. This effect was not observed for transh-down bin triads.
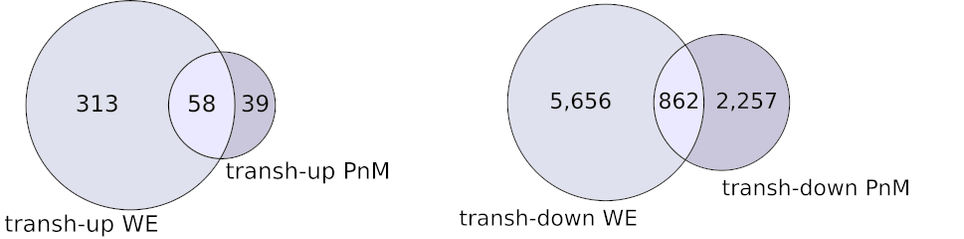
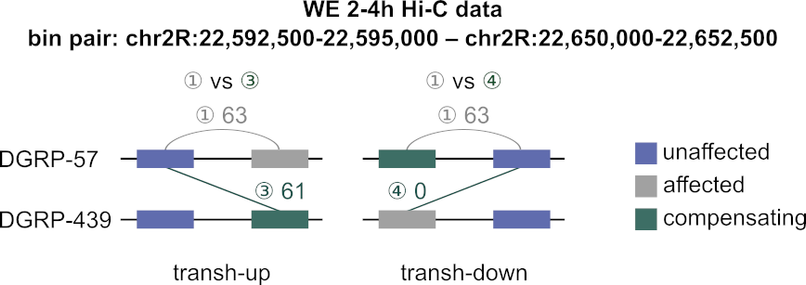
3/7 While transh-down interactions are more common, we show that the transh-up ones are more interesting. First, let’s note that the majority of transh-up triads identified in cell line (PnM) are also found to be transh-up in 2-4 h embryos (WE).
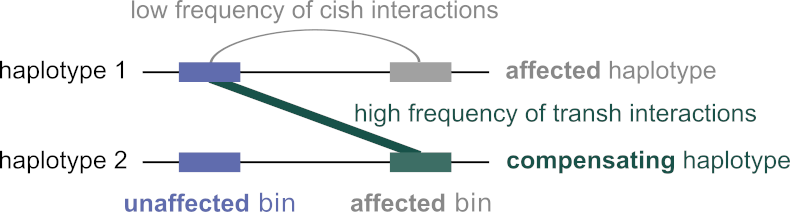
2/7 We identified triads of genomic elements (bins) enriched or depleted in transh interactions (transh-up or transh-down) using phased Hi-C data from heterozygotic Drosophila melanogaster cells: whole embryos (WE) and a differentiated cell line (PnM).
Our #genomics #bioRxiv preprint with Magdalena Machnicka is out!
Trans-homologous interactions identified in Hi-C data are associated with embryonic development https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2025.04.25.648339v1
Chromatin contacts between homologous chromosomes are widespread in the fruit fly and also present in other organisms. But what does it mean if trans-homologous (transh) contacts are enriched compared to the cis-homologous (cish) ones?