3️⃣/ However, @carlipeters.bsky.social's #ZooMS work in 30°C Australian caves found 70,000-year-old collagen from extinct fauna. This challenges our models and suggests preservation mechanisms we don't fully understand. Environmental factors clearly matter more than temperature alone.
#zooms
🧵 Thread: 1️⃣ Fascinating paper by Stewart et al. shows robust method for sex determination using peptides in tooth enamel. Great potential for #archaeology with fragmentary remains where DNA is degraded. #palaeoproteomics #ZooMS #teammasspec figshare.com/s/a861c0d74d...
2025 @nhsf.bsky.social 1st annual conference 10th July 2025
Call for Posters!
Deadline 30th April 2025.
Excellent opportunity for #palaeoproteomics, #ZooMS researchers. A diverse range of heritage science. Great for PhD students and ECRs.
www.heritagescienceforum.org.uk/what-we-do/2...
Posters | National Heritage Sc...
3/4 The role involves:
Managing thousands of parchment samples
Operating liquid handling robots
Performing #ZooMS analysis with MALDI-TOF MS
Generating DNA libraries from ancient samples
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ZooMS
ZooMS - Wikipedia
🧵 Thread: 1️⃣ Excited to announce the next ICAZ Archaeozoology, Genetics, Proteomics & Morphometrics (AGPM) working group meeting in Copenhagen, Denmark, Oct 14-17, 2025! #palaeoproteomics #ZooMS #archaeology
sites.google.com/palaeome.org...
ICAZ AGPM 2025
7/9 The curated CollagenDB database at the heart of the pipeline includes 614 species across multiple taxonomic groups, far broader than typical ZooMS approaches. A significant resource for the community. #ZooMS
🧵 Thread: 1/9 Important new paper! "Classification of Collagens via Peptide Ambiguation in a Paleoproteomic LC-MS/MS-Based Taxonomic Pipeline" by Ian Engels, @archaeoalex.bsky.social and team. Read it: pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/... #palaeoproteomics #ZooMS
Classification of Collagens vi...
4/5 🧠 Challenging peptide: COL1ɑ2 978-990 (peptide A) crucial for distinguishing reindeer from Bos/Bison. Study shows m/z 1192.6796 is critical for Bos/Bison ID, while m/z 1166.6276 indicates reindeer even when other markers absent. #ZooMS
🧵 Thread: Comparing mass analyzers for ZooMS on poorly preserved collagen 1/5 Raymond et al. @palaeocdf.bsky.social @archaeoprotein.bsky.social test MALDI-TOF vs MALDI-FTICR for ZooMS analysis on Palaeolithic bone fragments (37-34 ka BP). Paper: doi.org/10.1002/rcm.... #ZooMS
🧵 Thread: 1️⃣ New paper by@jessiehendy.bsky.social Blacka et al. presents breakthrough in rapid proteomic amelogenin sex estimation using Evosep-timsTOF MS. Slashes analysis time to under 20 mins per sample (including prep)! #palaeoproteomics #ZooMS doi.org/10.1002/rcm....
Rapid Proteomic Amelogenin Sex...
1️⃣ 🧵 Thread: GBE: "Phylogenetic Signal in Primate Tooth Enamel Proteins..." by Fong-Zazueta, @johannakrueger.bsky.social et al. Study on enamelome phylogenetic reliability. #palaeoproteomics #ZooMS doi.org/10.1093/gbe/...
Phylogenetic Signal in Primate...
@whatkatiedigs.bsky.social has a funded PhD opportunity @uniofaberdeen.bsky.social
Using #ZooMS and #sedaDNA #ancientDNA, #radiocarbon dating and #geoarchaeology to find Scotland's lost Ice Age animals 🦣❄️
#PhDposition #archaeology #paleontology #biomolecular
Finding Scotland’s Lost Ice Ag...
🧬 "Bulk bone Shotgun Metagenomics" #BBSMG* reveals 8thC 🐟 trade across the Himalayas. Crushed bone fragments identified S Asian species (Rohu) at high-altitude Tibetan site interesting to compare #ZooMS vs #BBSMG doi.org/10.1016/j.ja... *aka Scrapheap Challenge www.nature.com/articles/sre...
🦆 2/5 The team found unexpected protein variations within the SAME species - like 15 different versions in mallard ducks alone! Paleoproteomics often tries to ID ancient species by matching protein sequences...🤔 Plus, variations in ALL 13 proteins they studied. Can see why #ZooMS uses collagen!
The HPB-MALDI team dropped an open database of 11,055 mass spec signatures from pathogenic bacteria. #ZooMS folks - could this be a useful roadmap for making our data truly open & accessible? Everything on #Zenodo - a useful template for a #ZooMS DB 💽. www.nature.com/articles/s41...
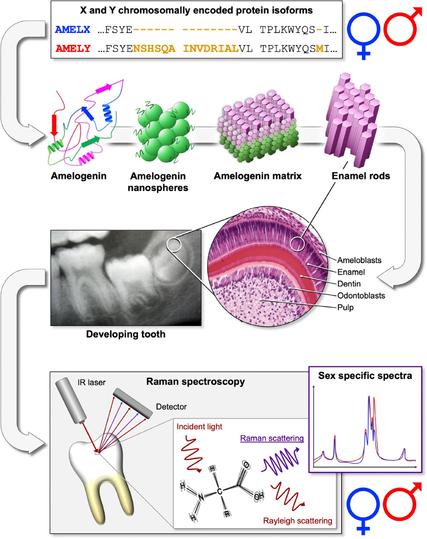
2/5 Key techniques: #ZooMS: Fast species ID using collagen fingerprints SPIN: Enhanced taxonomic resolution via proteome analysis Dental enamel proteomics 🦷: Sex determination from AMELX/Y proteins (see the new paper by @palaeoprotpalesa.bsky.social!) Full proteome: Some phylogenetic insight
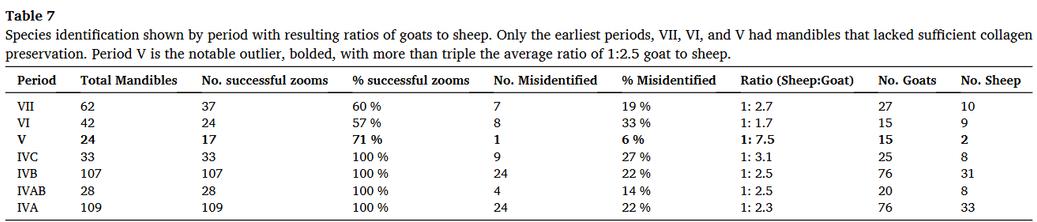
🏺 @suziebirch.bsky.social demonstrates that combining #ZooMS (88%) + morphology (76%) reveals hidden insights into ancient sheep/goat differences at Tepe Yahya, Iran Contradicts previous studies: 🐑 more often misidentified than 🐐 www.sciencedirect.com/science/arti... #teammassspec
The #palaeoproteomics #ZooMS starter pack has been updated to include, amongst others
@archaeoprotein.bsky.social and @drsambrown.bsky.social
RE: https://bsky.brid.gy/convert/ap/at://did:plc:2yli6spsnibim6g6cpziedd6/app.bsky.graph.starterpack/3lbkpaxeohz2p
Help wanted. I have purchased a wallaby hide to make it into standards for #ZooMS. The selection of wallaby was to target a species that is not widely studied. It is veg-tanned leather, species unknown. What forms of standards should we prepare - gelatin, collagen shavings, leather, parchment?
3 year PostDoc Tuebingen (+Sam Brown)
#ZooMS in Southern Africa Project.
Deadline March 15th 2025
Three-year position for a rese...