@stevenfeldman @milhaud Steven, can I welcome you to Spain? My Sabadell experience there is ok. Personal banker contact, not had in 25 years in NL, in Motril branch. App requires some patience, extra settings for smooth transactions, ok, but not disruptive.
Free source geospatial professional. Maphacker and mapmaker. GeoPythonist. Occasional blogger at https://justobjects.nl . My mapwork at https://map5.nl and https://map5topo.nl. OSGeo Charter member and founder/former chair OSGeo.nl. Learning Spanish.
Presented "Natural Navigation", at MapTime AMS Meetup at TomTom. No more screen-staring, relearn orientation, reconnect to nature...Thanks Tristan Gooley!
Slides: https://files.justobjects.nl/presentation/maptime-2025/maptime-natural-nav-2025-v1.pdf
Versie 25 Jun 2025 "OpenStreetMap Database (PostGIS) Dumps Nederland en aangrenzend Buitenland" beschikbaar op https://geotoko.nl. Zie GeoCatalogus:
https://geocatalogus.nl/dataset/osm-nederland-database-dumps
#geonl #openstreetmap #osgeonl
Are you curious about the "Future of GIS"? If yes, tune in to episode 290. of the **#geomobpod **to hear about discrete global grid systems from Instituto Superior Técnico lecturer @luis_de_sousa.
He provides an overview of what DGG systems are, the challenges of existing systems like H3 and why they could prove to be so important in the future.
Enjoy:
@geogoeroe @gspeed0689 the answer is no, not yet. See this long-running topic on OSM-NL:
https://community.openstreetmap.org/t/instance-panoramax-nederland/115829 . Organization, hands and some money needed...
@jorgesanz he comprado un Sangean (Taiwanese). Creo modelo MMR-99. Manivela, solar, USB, luz de alarm. Un poco caro, pero es también un 'Bluetooth Box' con un sonor bien.
Ver: https://www.conrad.com/en/search.html?search=sangean%20mmr-99 . (escrito sin traducador).
Alle BRT PostGIS Datadumps van 14 Jun 2025 zijn beschikbaar op https://geotoko.nl Dus de TOP10, 50, 100, 250, 500 en 1000NL. Zie ook GeoCatalogus: https://geocatalogus.nl/dataset?tags=BRT
#geonl
Alle BAG (v2) producten (PostGIS, Adressen CSVs BAG Compact) versie 08 Jun 2025 nu op https://geotoko.nl.
Inclusief het nieuwe "Panden Plus" product. Zie ook de GeoCatalogus voor al onze BAG producten:
https://geocatalogus.nl/dataset?tags=BAG
#geonl #osgeonl
Meteen een debat aangevraagd met de minister. We gaan ons niet de Amerikaanse Cloud in laten rommelen, omdat het kabinet gevallen is! Het standpunt van de #tweedekamer is heel duidelijk, we gaan voor de NederCloud! https://berthub.eu/articles/posts/demissionair-de-cloud-in-denderen/
UPDATE 2: We're carefully back online again, with a few exceptions:
https://mapstodon.space/@lokjo/114657821935053517
Can we have a lill boost please? The fediverse is the only place we're on.
We're a replacement for googlemaps.
European, non-commercial, pro-local.
Thanks for sharing 😊
De BGT PostGIS data dump stand 04 Jun 2025 beschikbaar op https://geotoko.nl. Zie GeoCatalogus:
https://geocatalogus.nl/dataset/bgt-imgeo-database-dumps
#geonl #pdok #nlextract
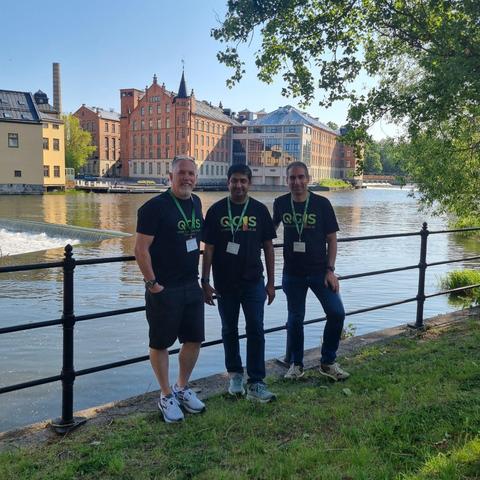
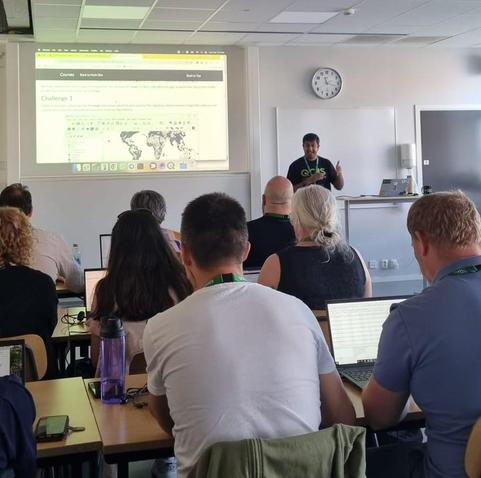
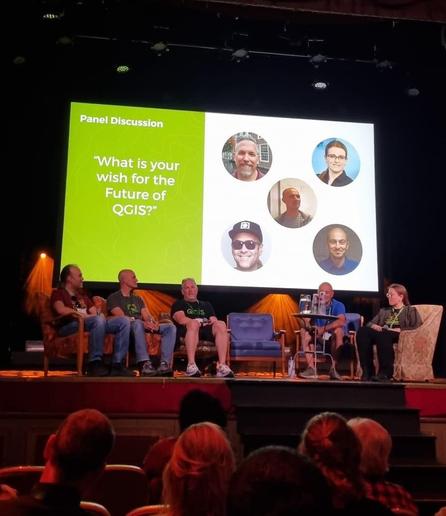
This week, I’m at #qgisuc2025 in Norrköping, Sweden! Monday and Tuesday, I've enjoyed inspiring talks and hands-on workshops. A huge thank you to the organizing committee for putting together such a fantastic event and making it all possible! 👏
Today, I'm giving a workshop on hydrological analysis tools in QGIS—follow along at @gisocw https://courses.gisopencourseware.org/course/view.php?id=75
Thursday & Friday I'll join the QGIS Contributor Meeting to collaborate on improving QGIS!
Why Bell Labs worked so well, and could innovate so much, while today’s innovation, in spite of the huge private funding, goes in hype-and-fizzle cycles that leave relatively little behind, is a question I’ve been asking myself a lot in the past years.
And I think that the author of this article has hit the nail on its head on most of the reasons - but he didn’t take the last step in identifying the root cause.
What Bell Labs achieved within a few decades is probably unprecedented in human history:
They employed folks like Nyquist and Shannon, who laid the foundations of modern information theory and electronic engineering while they were employees at Bell.
They discovered the first evidence of the black hole at the center of our galaxy in the 1930s while analyzing static noise on shortwave transmissions.
They developed in 1937 the first speech codec and the first speech synthesizer.
They developed the photovoltaic cell in the 1940, and the first solar cell in the 1950s.
They built the first transistor in 1947.
They built the first large-scale electronic computers (from Model I in 1939 to Model VI in 1949).
They employed Karnaugh in the 1950s, who worked on the Karnaugh maps that we still study in engineering while he was an employee at Bell.
They contributed in 1956 (together with AT&T and the British and Canadian telephone companies) to the first transatlantic communications cable.
They developed the first electronic musics program in 1957.
They employed Kernighan, Thompson and Ritchie, who created UNIX and the C programming language while they were Bell employees.
And then their rate of innovation suddenly fizzled out after the 1980s.
I often hear that Bell could do what they did because they had plenty of funding. But I don’t think that’s the main reason. The author rightly points out that Google, Microsoft and Apple have already made much more profit than Bell has ever seen in its entire history. Yet, despite being awash with money, none of them has been as impactful as Bell. Nowadays those companies don’t even innovate much besides providing you with a new version of Android, of Windows or the iPhone every now and then. And they jump on the next hype wagon (social media, AR/VR, Blockchain, AI…) just to deliver half-baked products that (especially in Google’s case) are abandoned as soon as the hype bubble bursts.
Let alone singlehandedly spear innovation that can revolutionize an entire industry, let alone make groundbreaking discoveries that engineers will still study a century later.
So what was Bell’s recipe that Google and Apple, despite having much more money and talented people, can’t replicate? And what killed that magic?
Well, first of all Bell and Kelly had an innate talent in spotting the “geekiest” among us. They would often recruit from pools of enthusiasts that had built their own home-made radio transmitters for fun, rather than recruiting from the top business schools, or among those who can solve some very abstract and very standardized HackerRank problems.
And they knew how to manage those people. According to Kelly’s golden rule:
How do you manage genius? You don’t
Bell specifically recruited people that had that strange urge of tinkering and solving big problems, they were given their lab and all the funding that they needed, and they could work in peace. Often it took years before Kelly asked them how their work was progressing.
Compare it to a Ph.D today who needs to struggle for funding, needs to produce papers that get accepted in conferences, regardless of their level of quality, and must spend much more time on paperwork than on actual research.
Or to an engineer in a big tech company that has to provide daily updates about their progress, has to survive the next round of layoffs, has to go through endless loops of compliance, permissions and corporate bureaucracy in order to get anything done, has their performance evaluated every 3 months, and doesn’t even have control on what gets shipped - that control has been taken away from engineers and given to PMs and MBA folks.
Compare that way of working with today’s backlogs, metrics, micromanaging and struggle for a dignified salary or a stable job.
We can’t have the new Nyquist, Shannon or Ritchie today simply because, in science and engineering, we’ve moved all the controls away from the passionate technical folks that care about the long-term impact of their work, and handed them to greedy business folks who only care about short-term returns for their investors.
So we ended up with a culture that feels like talent must be managed, even micromanaged, otherwise talented people will start slacking off and spending their days on TikTok.
But, as Kelly eloquently put it:
“What stops a gifted mind from just slacking off?” is the wrong question to ask. The right question is, “Why would you expect information theory from someone who needs a babysitter?”
Or, as Peter Higgs (the Higgs boson guy) put it:
It’s difficult to imagine how I would ever have enough peace and quiet in the present sort of climate to do what I did in 1964… Today I wouldn’t get an academic job. It’s as simple as that. I don’t think I would be regarded as productive enough.
Or, as Shannon himself put it:
I’ve always pursued my interests without much regard for final value or value to the world. I’ve spent lots of time on totally useless things.
So basically the most brilliant minds of the 20th century would be considered lazy slackers today and be put on a PIP because they don’t deliver enough code or write enough papers.
So the article is spot on in identifying why Bell could invent, within a few years, all it did, while Apple, despite having much more money, hasn’t really done anything new in the past decade. MBAs, deadlines, pseudo-objective metrics and short-termism killed scientific inquiry and engineering ingenuity.
But the author doesn’t go one step further and identify the root cause.
It correctly spots the business and organizational issues that exist in managing talent today, but it doesn’t go deeper into their economic roots.
You see, MBA graduates and CEOs didn’t destroy the spirit of scientific and engineering ingenuity spurred by the Industrial Revolution just because they’re evil. I mean, there’s a higher chance for someone who has climbed the whole corporate ladder to be a sociopath than there is for someone you randomly picked from the street, but not to the point where they would willingly tame and screw the most talented minds of their generation, and squeeze them into a Jira board or a metric that looks at the number of commits, out of pure sadism.
They did so because the financial incentives have drastically changed from the times of Bells Labs.
The Bells Labs were basically publicly funded. AT&T operated the telephone lines in the US, paid by everyone who used telephones, and they reinvested a 1% tax into R&D (the Bells Labs). And nobody expected a single dime of profits to come out from the Bells Labs.
And btw, R&D was real R&D with no strings attached at the time. In theory also my employer does R&D today - but we just ended up treating whatever narrow iterative feature requested by whatever random PM as “research and development”. It’s not like scientists have much freedom in what to research or engineers have much freedom in what to develop. R&D programs have mostly just become a way for large businesses to squeeze more money out of taxpayers, put it in their pockets, and not feel any moral obligation of contributing to anything other than their shareholders’ accounts.
And at the time the idea of people paying taxes, so talented people in their country could focus on inventing the computer, the Internet or putting someone on the moon, without the pressure of VCs asking for their dividends, or PMs asking them to migrate everything to another cloud infrastructure by next week, or to a new shiny framework that they’ve just heard in a conference, wasn’t seen as a socialist dystopia. It was before the neoliberal sociopaths of the Chicago school screwed up everything.
The America that invested into the Bell Labs and into the Apollo project was very different from today’s America. It knew that it was the government’s job to foster innovation and to create an environment where genuinely smart people could do great things without external pressure. That America hadn’t yet been infected by the perverse idea that the government should always be small, that it’s not the government’s job to make people’s lives better, and that it was the job of privately funded ventures seeking short-term returns to fund moonshots.
And, since nobody was expecting a dime back from Bell, nobody would put deadlines on talented people, nobody hired unqualified and arrogant business specialists to micromanage them, nobody would put them on a performance improvement plan if they were often late at their daily standups or didn’t commit enough lines of code in the previous quarter. So they had time to focus on how to solve some of the most complex problems that humans ever faced.
So they could invent the transistor, the programming infrastructure still used to this day, and lay the foundations of what engineers study today.
The most brilliant minds of our age don’t have this luxury. So they can’t revolutionarize our world like those in the 20th century did.
Somebody else sets their priorities and their deadlines.
They can’t think of moonshots because they’re forced to work on the next mobile app riding the next wave of hype that their investors want to release to market so they can get even richer.
They have to worry about companies trying to replace them with AI bots and business managers wanting to release products themselves by “vibe coding”, just to ask those smart people to clean up the mess they’ve done, just like babies who are incapable of cleaning up the food they’ve spilled on the floor.
They are seen as a cost, not as a resource. Kelly used to call himself a “patron” rather than a “manager”, and he trusted his employees, while today’s managers and investors mostly see their engineering resources as squishy blobs of flesh standing between their ambitious ideas and their money, and they can’t wait to replace them with robots that just fullfill all of their wishes.
Tech has become all about monetization nowadays and nothing about ingenuity.
As a result, there are way more brilliant minds (and way more money) in our age going towards solving the “convince people to click on this link” problem rather than solving the climate problem, for example.
Then of course they can’t invent the next transistor, or bring the next breakthrough in information theory.
Then of course all you get, after one year of the most brilliant minds of our generation working at the richest company that has ever existed, is just a new iPhone.
https://links.fabiomanganiello.com/share/683ee70d0409e6.66273547
Ha, het verslag is nu al op opentk.nl! https://berthub.eu/tkconv/verslag.html?vergaderingid=6989c6a4-bf75-45f8-8bbe-2f0618d307a3
New release of OWSLib, a Python package for client programming with OGC web services https://github.com/geopython/OWSLib/releases/tag/0.34.0 #python #foss4g #osgeo #ogc
Ik heb de Mastodon-draad met het live verslag van het nota overleg over de initiatiefnota van @barbarakathmann en Jesse Six Dijkstra "Wolken aan de Horizon" omgezet tot een blogpost, voor de mensen die de weg naar Mastodon nog niet gevonden hebben! https://berthub.eu/articles/posts/verslagje-nota-overleg-wolken-aan-de-horizon/
Meer digitale onafhankelijkheid is noodzakelijk voor onze veiligheid nu en in de toekomst. Samen met Jesse Six Dijkstra van NSC verdedig ik vandaag ons initiatief voor een Nederlandse cloud. Meekijken kan hier vanaf 10:00 uur 👉🏻 https://www.tweedekamer.nl/vergaderingen/livedebat/thorbeckezaal
https://groenlinkspvda.nl/nieuws/initiatiefnota-nederlandse-cloud/
Present in de Tweede Kamer! Behoorlijke opkomst bij het publiek, en 7 kamerleden van GL-PvdA VVD Volt PVV en NSC.
Delighted to share that the Geomob organizers in Belgium 🇧🇪 (Ben Abelshausen @xivk and Han Tambuyzer) have set the date for the next event: join them on 🗓️ Tuesday, 3rd of June - this time in Brussels!
Sign-up is open, and speaker volunteers are needed.
Full details: https://thegeomob.com/post/june-03-2025-geomobbe-details
De BRK-DKK (Digitale Kadastrale Kaart van PDOK-Kadaster), stand van 01 Jun 2025 beschikbaar als PostGIS Dump op https://geotoko.nl.
Zie ook de GeoCatalogus: https://geocatalogus.nl/dataset/brk-digitale-kadastrale-kaart-dkk-database-dumps
#geonl #osgeonl #nlextract