🛠️ Tool
===================
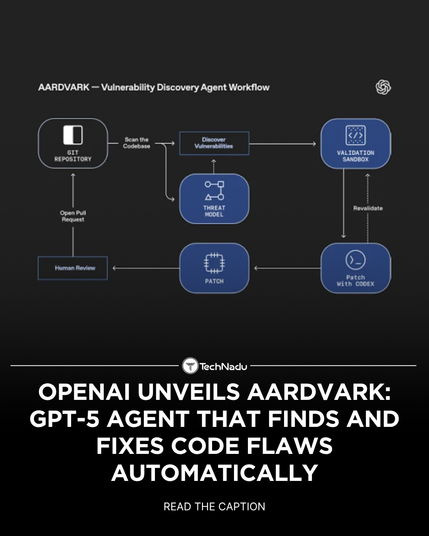
Executive summary: OpenAI released Aardvark, an invite-only Beta LLM-powered security model built on ChatGPT-5 that automates vulnerability discovery, prioritization, sandbox validation of exploitability, and proposed patch generation for source-code repositories. OpenAI reports that Aardvark found 92% of known and synthetic vulnerabilities in unspecified "golden" repositories and has identified 10 issues that received CVE entries.
Technical details:
• Aardvark explicitly contrasts itself with traditional program analysis: it "does not rely on fuzzing or software composition analysis (SCA)" and instead leverages LLM reasoning plus orchestrated tool use (reading code, synthesizing tests, running sandboxed checks, and annotating code).
• Features described include automated threat-model generation from repository contents, exploit sandboxing to validate real-world exploitability, inline code annotation, and submission of patch proposals for human review.
• Deployment and access are described as invite-only Beta with plans to expand; open-source noncommercial repositories are slated to receive free scanning access.
How it works conceptually:
• LLM reasoning layer ingests code and repository metadata to generate hypotheses about vulnerable behavior.
• Orchestrator issues targeted tests and leverages sandboxed execution to confirm exploitability before producing remediation suggestions.
• Outputs include vulnerability prioritization and human-reviewable patches rather than fully autonomous commits.
Detection and validation guidance (conceptual):
• Focus detection on logic/semantic patterns the model highlights (e.g., insecure use of deserialization, improper auth checks, information leaks) and validate model-suggested exploitability with isolated test harnesses.
• Treat proposed patches as candidate fixes requiring code-review and threat-model re-evaluation; track CVE assignments reported by the tool.
Limitations and open questions:
• Reported evaluation used unspecified "golden" repositories; details on dataset composition, false-positive/false-negative rates beyond the 92% figure are not published.
• Reliance on LLM reasoning raises questions about reproducibility and the potential for hallucinated fixes; OpenAI states patches are submitted for human review.
• Disclosure policy changes at OpenAI (no strict timelines) may affect coordinated reporting cadence and public visibility of findings.
Takeaway: Aardvark represents an LLM-driven shift toward automated detection+validation+remediation workflows, with promising early metrics and open questions about evaluation details and operational controls. #Aardvark #OpenAI #tool
🔗 Source: https://cyberscoop.com/openai-aardvark-security-and-patching-model-beta/