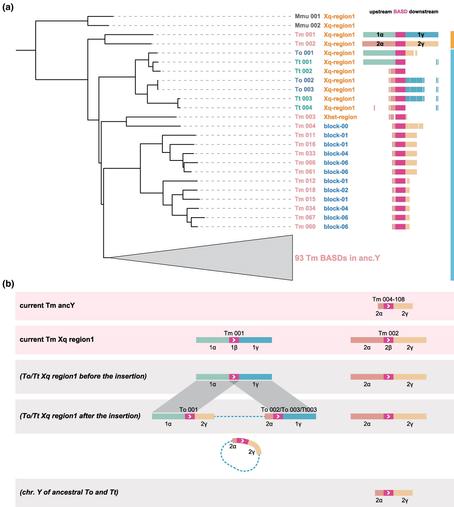
Population genomic analysis of common marmosets by Soni et al., taking into account twin births and hematopoietic chimerism, indicates a demographic contraction ~7,000 years ago, coinciding with ecological shifts in northeastern Brazil.
🔗 doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msaf119