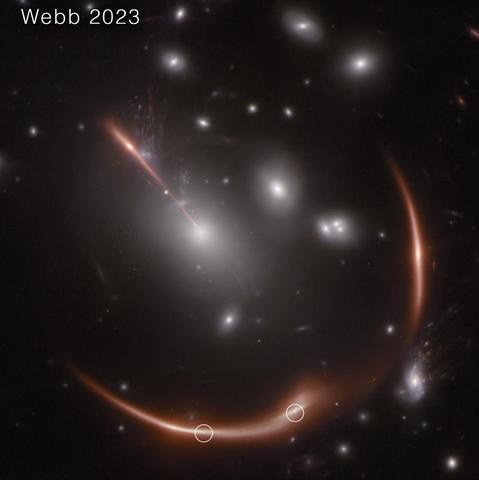
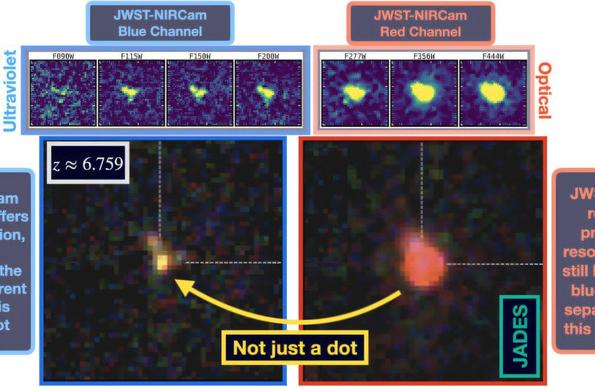
I dati infrarossi del telescopio James Webb rivelano ulteriori dettagli strutturali del getto del buco nero di M87
Sebbene M87 sia stata oggetto di moltissime osservazioni, i dati nello spettro infrarosso erano relativamente scarsi. Ma un gruppo di scienziati ha utilizzato il telescopio James Webb e le sue camere nel vicino infrarosso (NIRCam) per risolvere alcuni dettagli precedentemente sfocati del getto di M87.
https://umbertogaetani.substack.com/p/i-dati-infrarossi-del-telescopio