Weekly Update from the Open Journal of Astrophysics – 20/06/2025
Yesterday (Thursday 19th June 2025) was a national holiday in the USA, which means that no new papers were announced on arXiv today (Friday 20th June). I have therefore decided to bring forwarded the usual weekly update of papers published at the Open Journal of Astrophysics by a day. Since the last update we have published three new papers, which brings the number in Volume 8 (2025) up to 74, and the total so far published by OJAp is now up to 309.
The three papers published this week, with their overlays, are as follows. All three were published on Tuesday, June 17th 2025. You can click on the images of the overlays to make them larger should you wish to do so.
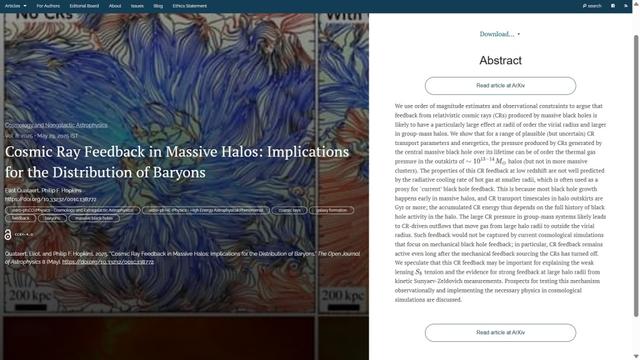
The first paper to report is “Illuminating the Physics of Dark Energy with the Discovery Simulations” by Gillian D. Beltz-Mohrmann (Argonne National Laboratory, USA) and 12 others based in the USA and Spain. This describes new high-resolution cosmological simulations providing a testbed for alternative cosmological probes that may offer additional constraining power beyond Baryon Accoustic Oscillations. It is filed in the folder marked Cosmology and NonGalactic Astrophysics.
The overlay is here:
You can read the final accepted version on arXiv here.
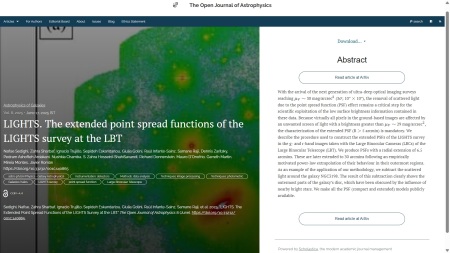
The second paper is in the folder marked Astrophysics of Galaxies. It is “LIGHTS. The extended point spread functions of the LIGHTS survey at the LBT” by Nafise Sedighi (Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias, Spain) and 15 others based in Spain, USA, Iran, Italy and the UK. It describes the procedure used to construct the extended Point Spread Functions (PSFs) of the LIGHTS survey in images taken with the Large Binocular Cameras (LBCs) of the Large Binocular Telescope (LBT).
The overlay is here:
You can find the officially-accepted version of the paper on arXiv here.
Finally this week we have “Fast radio bursts as a probe of gravity on cosmological scales” by Dennis Neumann (Leiden University, Netherlands), Robert Reischke (Universität Bonn, Germany), Steffen Hagstotz (Ludwig-Maximilians Universität München, Germany) and Hendrik Hildebrandt (Ruhr University Bochum, Germany). This is about using dispersion measures derived from Fast Radio Bursts (FRBs) in combination with cosmic shear to investigate modified gravity theories, specifically Horndeski gravity. It is in the folder marked Cosmology and NonGalactic Astrophysics.
The overlay is here:
You can find the officially-accepted version on arXiv here.
That’s all the papers for this week. I’ll revert to the usual schedule for updates next week, and post the next one on Saturday 28th June.
#arXiv240911163v3 #arXiv241020190v2 #arXiv250305947v2 #AstrophysicsOfGalaxies #cosmicShear #Cosmology #CosmologyAndNonGalacticAstrophysics #DiamondOpenAccessPublishing #DiscoverySimulations #fastRadioBursts #HorndeskiGravity #LargeBinocularTelescope #LIGHTSSurvey #OpenJournalOfAstrophysics #PointSpreadFunction #TheOpenJournalOfAstrophysics