Wireless Security Protocols Explained: WEP, WPA, WPA2 & WPA3 📡🔐
Understanding wireless security protocols is essential for protecting your network from unauthorized access and ensuring data confidentiality.
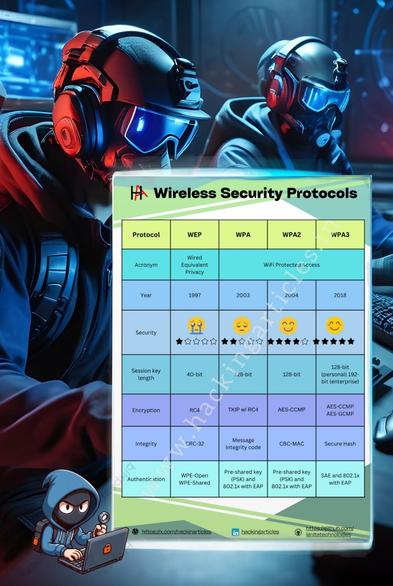
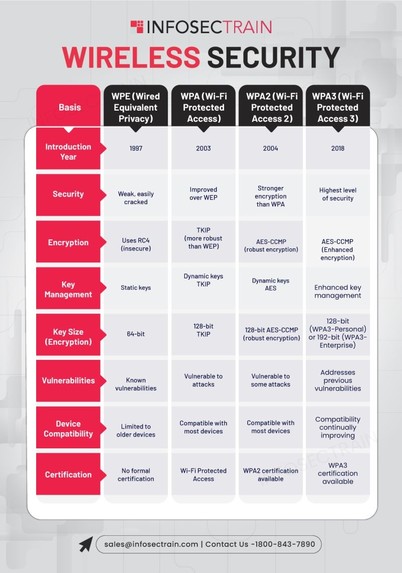
📘 Key Protocols & Their Characteristics:
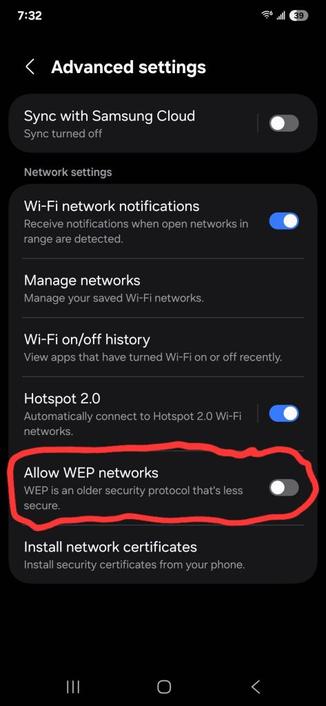
1. WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy)
• Introduced in 1997
• Weak encryption (RC4), easily cracked
• Deprecated and insecure
2. WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access)
• Interim solution after WEP
• Improved encryption with TKIP
• Still vulnerable to certain attacks
3. WPA2
• Widely used today
• Uses AES-based CCMP encryption
• Supports enterprise (RADIUS) and personal (PSK) modes
4. WPA3
• Latest standard with stronger security
• Resistant to brute-force attacks
• Supports SAE (Simultaneous Authentication of Equals)
• Enhanced encryption and forward secrecy
Why it matters:
Choosing the right wireless protocol significantly affects your network’s resilience against common attack vectors such as packet sniffing, replay attacks, and credential theft.
Disclaimer: This post is for educational and awareness purposes only. Always secure your wireless networks using the latest standards.
#WirelessSecurity #WPA3 #WEP #WPA2 #CyberSecurity #InfoSec #EducationOnly #WiFiProtocols #NetworkSecurity #WiFiEncryption