Loss of sea ice alters the colors of light in the ocean
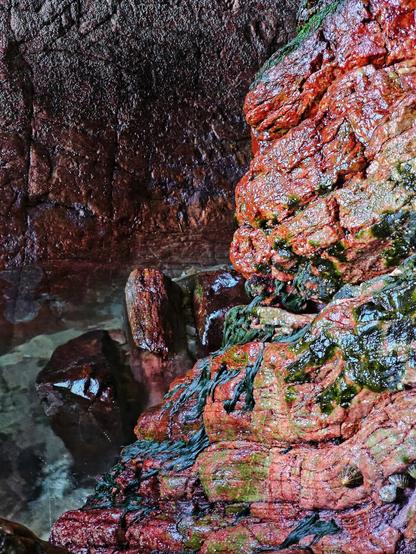
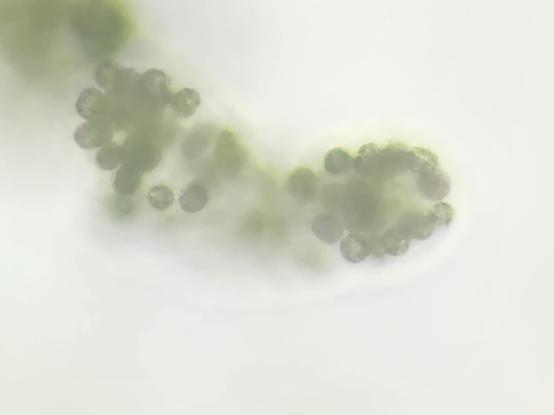
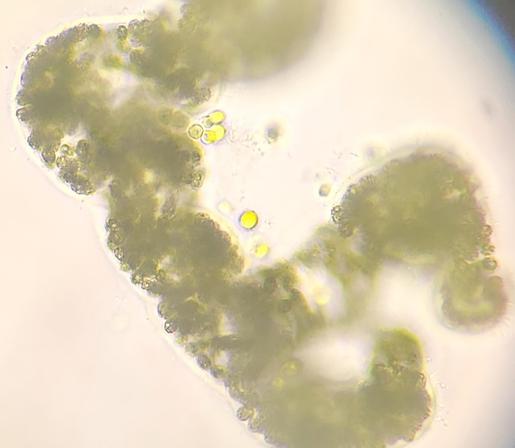
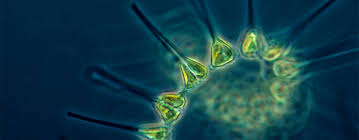
The disappearance of sea ice in polar regions due to #GlobalWarming not only increases the amount of light entering the #ocean, but also changes its #color. These changes have far-reaching consequences for #photosynthetic organisms such as ice #algae and #phytoplankton.
That is the conclusion of new research published in Nature Communications, led by marine biologists Monika Soja-Woźniak and Jef Huisman from the Institute for Biodiversity and Ecosystem Dynamics (IBED) at the University of Amsterdam.
The international research team, which also included physical chemist Sander Woutersen (HIMS/UvA) and collaborators from the #Netherlands and #Denmark, investigated how the loss of #SeaIce alters the underwater light #environment. Sea ice and #seawater differ fundamentally in how they transmit light. Sea ice strongly scatters light and reflects much of it, while allowing only a small amount to penetrate.
Yet, this limited amount of light still contains almost the full range of visible wavelengths. In contrast, seawater absorbs red and green light, while blue light penetrates deep into the water column. This is what gives the ocean its blue color.