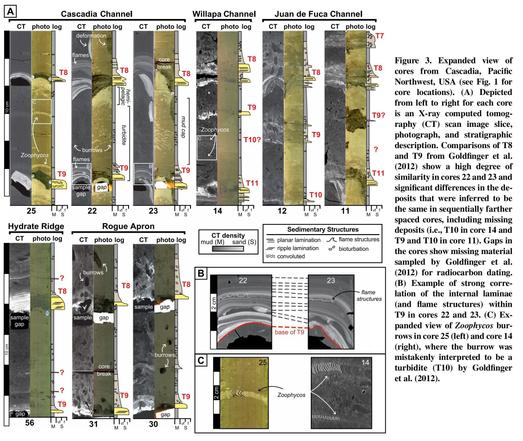
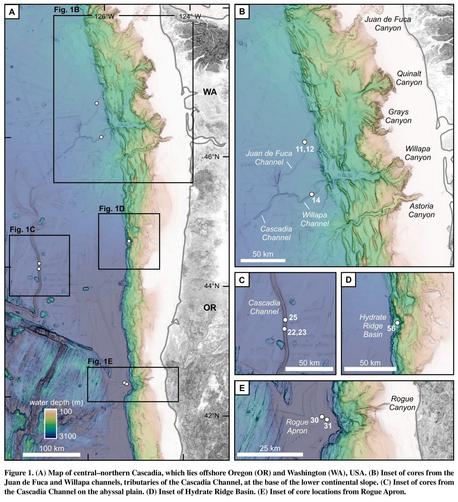
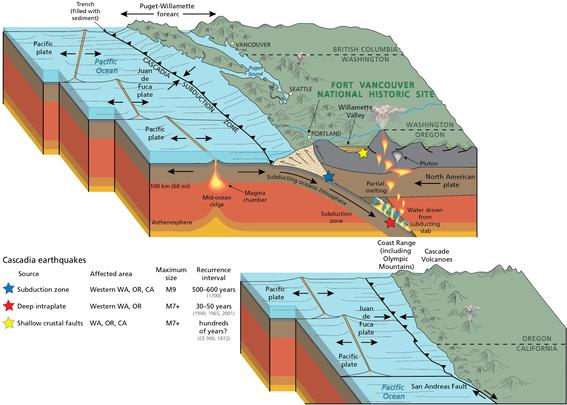
Algorithm Raises New Questions About Cascadia Earthquake Record
--
https://phys.org/news/2024-08-algorithm-cascadia-earthquake.html <-- shared technical article
--
https://doi.org/10.1130/B37343.1 <-- shared paper
--
#GIS #spatial #mapping #sedimentology #geology #structuralgeology #platetectonics #CascadiaSubductionZone #PNW #PacificNorthwest #spatialanalysis #spatiotemporal #forests #tsunamis #earthquake #risk #hazard #timing #naturaldisasters #geomorphology #geomorphometry #turbidite #corrleation #causation #model #modeling #massmovement #landslides #algorithm #machinelearning #AI
#Turbidite
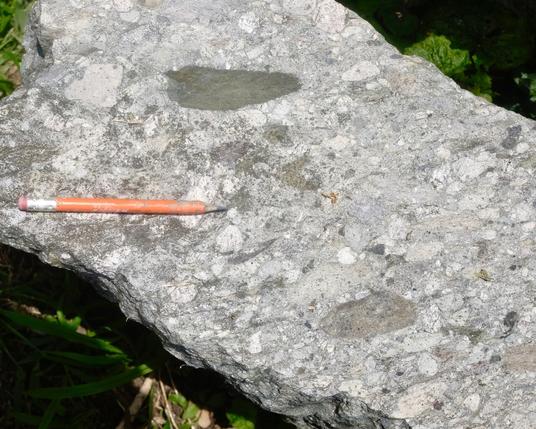
A small #outcrop of the #Squantum Member of the #Roxbury #Conglomerate
These #rocks are in the #BostonBay Group, which is currently dated to #Neoproterozoic. The Squantum Member was interpreted as a #tillite, possibly associated with the #Gaskiers #glaciation, although there a scant signs like scratched pebbles or faceted cobbles. It is currently commonly interpreted as a #debrite (debris flow). Details in captions.
#geology #glacier #turbidite #Quincy #Boston #Massachusetts #NewEngland
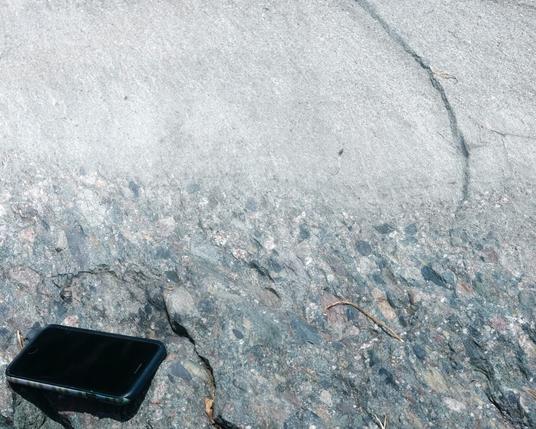
Anomalous pebble in layered #sedimentary #rock
An angular pebble is conformably surrounded by argillaceous and sandy layers in this #photograph of the #Neoproterozoic #Squantum Member of the #Roxbury Conglomerate. The wide range of clast sizes led to an interpretation as a #glacial #tillite thru the 1970s, but the Squantum Member is now mostly interpreted as a #debrisFlow (#debrite or #turbidite). My #photo.
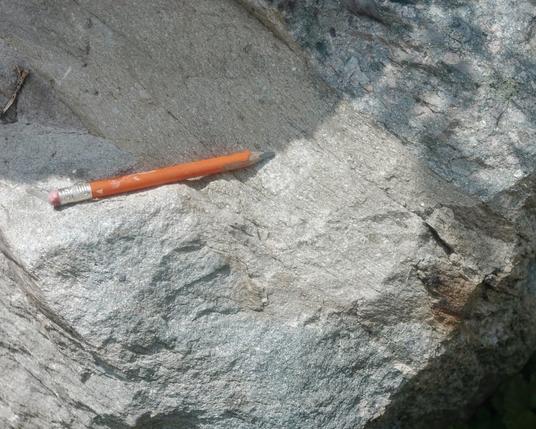
Deformed bedding in meta#sedimentary #rocks
The horizontal bedding of the #Squantum Member of the #Roxbury Conglomerate (#Neoproterozoic, #Boston Bay Group) has been disturbed locally.
In the #glacial #tillite interpretation of the Squantum (favored through at least the 1970s), the distortion might be caused by glaciotectonic drag at the ice base. The current interpretation as a #debrite or #turbidite would probably attribute the deformations to synsedimentary slumping. My #photo. #fieldTrip
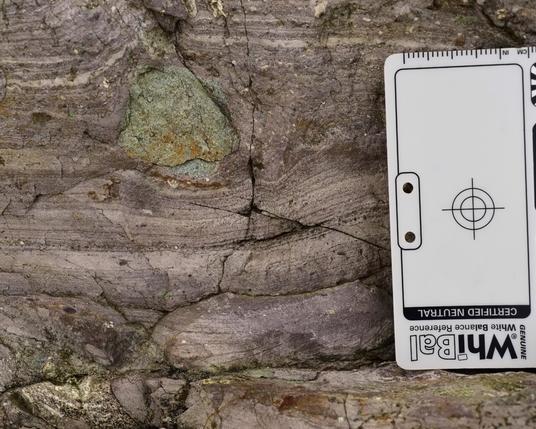
The #glacier went that-a-way
The #striations on this face of the #Ediacaran (ca. 560 Ma) #Squantum Member of the #Roxbury #Conglomerate were probably left by the #Pleistocene #Laurentide ice sheet, which retreated ca. 12 ka. The striations have the right orientation, from northwest to southeast.
The Squantum Member was once interpreted as a (#glacial) #tillite. The most common contemporary model is a peri-#Gondwana #debrite (#turbidite).
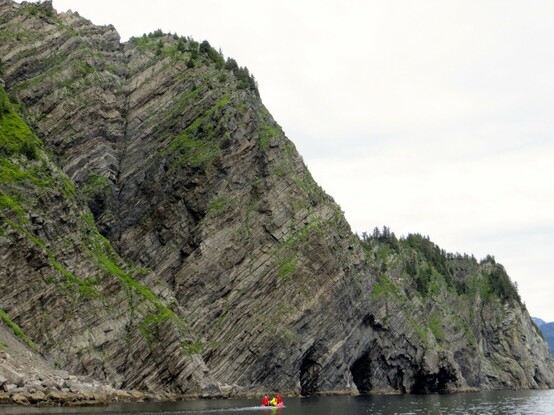
Turbidites above the Resurrection Peninsula Ophiolite, Alaska.
We now know that the turbidites on Fox Island, near Seward AK are part of the Paleocene Orca Group.
Spectacular in scale, and thickness.
Interbedded tuffaceous and fine grained siliciclastic layers in the Cambridge Argillite, a Neoproterozoic member of the Boston Bay Group, above the Roxbury Conglomerate. Usually interpreted as a turbidite distal to the Roxbury.