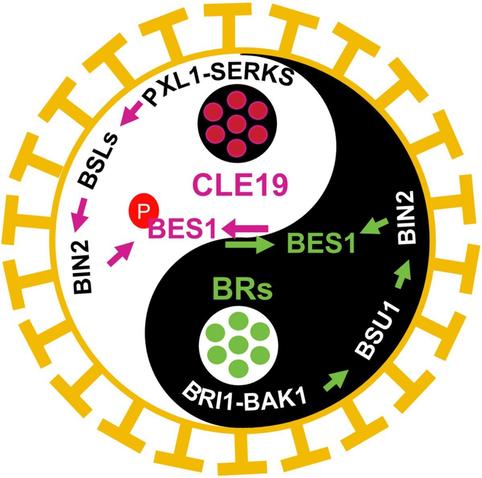
Wang et al. report that CLE19 suppresses brassinosteroid signaling output via the BSL-BIN2 module to maintain BES1 activity and #pollen exine patterning in #Arabidopsis.
🌺https://doi.org/10.1111/jipb.70024
@wileyplantsci
#PlantScience #plant #reproduction #hormone #OpenAccess #botany