Following #rstats packages were maintained and are back on #CRAN now thanks to Andrej Spiess
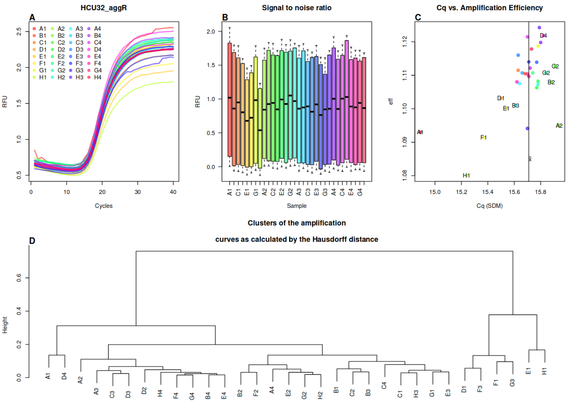
- #dpcR, 2025-06-18, Digital PCR Analysis <10.32614/CRAN.package.dpcR>
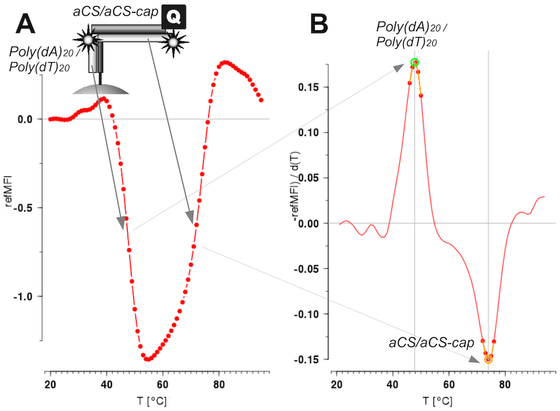
- #MBmca, 2025-06-11, Nucleic Acid Melting Curve Analysis (https://journal.r-project.org/articles/RJ-2013-024/)
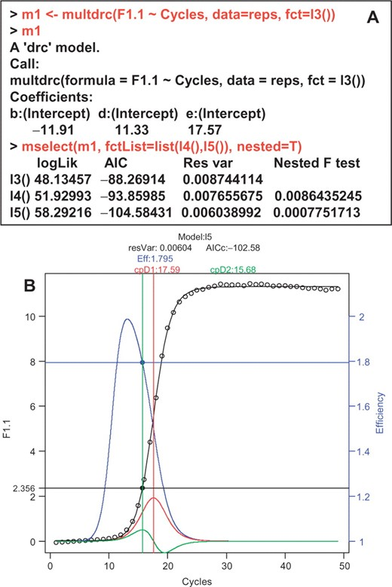
- #qpcR, 2025-06-10, Modelling and Analysis of Real-Time PCR Data <doi10.1093/bioinformatics/btn227>
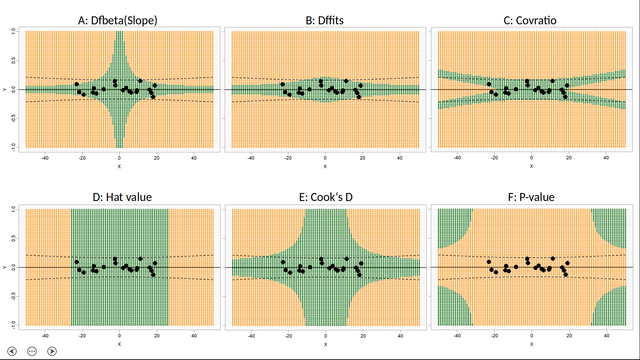
- #PCRedux, 2025-06-13, Quantitative #PCR (#qPCR) Data Mining and Machine Learning Toolkit as Described in <doi:10.21105/Joss.04407>