News from the battle between plants and viruses – our expert Samar Sheat summarises the success of fighting cassava diseases.
book your session: https://www.leibniz-gemeinschaft.de/ueber-uns/neues/veranstaltungen/book-a-scientist
#Pathogens
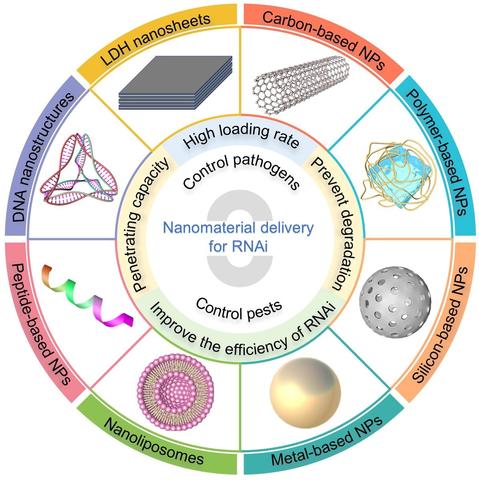
The cover of the May issue features a phoenix nanocarrier transporting RNAi "soldiers" who use their sharp spears to target and control #plant #pathogens, highlighting work on the potential of engineered nanotransporters for #RNAi delivery. https://www.jipb.net/EN/1672-9072/current.shtml
#PlantScience #Phytopathology #botany
🌱 International Day of Plant Health🌱
Today, we highlight an often-overlooked topic: plant health – vital for food security, biodiversity, and sustainable agriculture.
In our current research at Hochschule Bonn-Rhein-Sieg and Julius Kühn-Institute, we’re tackling a key question:
How can we detect plant diseases and pests before visible symptoms appear?
🔬 The answer: With the nose of chemistry!
We analyze volatile organic compounds (VOCs) that plants emit when under stress or attacked by
🦠 bacteria,
🍄 fungi, and
🪲 insect pests.
Using advanced GC-MS technology (gas chromatography-mass spectrometry), we aim to identify these unique molecular “scent signatures” and use them as an early-warning system to detect harmful organisms before they cause damage.
🧪 Our goal: to “sniff out” plant diseases and pests.
#PlantHealth #InternationalPlantHealthDay #VOCs #GCMS #EarlyDetection #Pathogens #InvasiveSpecies #AnalyticalChemistry #ScienceForSustainability #PlantPathogens #PlantProtection #VOCAnalysis
Today, the Hochschule Bonn-Rhein-Sieg University of Applied Sciences celebrated their 30th #anniversary.
Exactly half of that time I'm also a member of the University: first as a student (BSc, MSc), then as a PhD student and teaching staff member and now as a PostDoc.
During today's #science fair, I also presented our current #reasearch in #VOC #odor #detection for various #pathogens and #InvasiveSpecies
#h-brs #h_brs #bonn #rheinsieg #StAugustin #Rheinbach #forschung #planthealth #safetyresearch
SciTech Chronicles . . . .May 8th, 2025
#SIK3 #NSS #profile #kinase #pathogens #intercontinental #balloons #"35 kilometers" #"jurema preta" #dimethyltryptamine #"no ban" #"Mimosa tenuiflora" #TYK2 #psoriasis #inhibitor #signaling #Friendship #"Lamprotornis superbus" #reciprocal #DNA
Mass spectrometry method identifies pathogens within minutes instead of days
https://phys.org/news/2025-05-mass-spectrometry-method-pathogens-minutes.html
#HackerNews #massspectrometry #pathogens #rapiddiagnosis #healthcare #innovation
#PopulationGenetics of microbial #pathogens can inform decisions that impact society; @smlatorreo explores a @PLOSBiology study on wheat powdery mildew #fungus which uses genomic data to predict continental-scale dispersion routes. Paper: https://plos.io/43qfH9F Primer: https://plos.io/44YjHQN
How a Changing Climate Is Reshaping the Spread of Infectious Diseases
"...Then you have this convergence of crises—the #ClimateCrisis overlapping with the #PollutionCrisis. So you get this intersection between air pollution and respiratory #diseases, and then infectious diseases more broadly, all layered on top of a changing #climate.
When it comes to waterborne and foodborne diseases, the link to #ClimateChange is even more direct. As temperatures rise, you create more favorable conditions for #bacteria and other #pathogens to multiply. They thrive in warm environments—soil, water, contaminated areas—so warming can increase their abundance.
#ExtremeWeather events are also a big factor here. Aedes #mosquitoes need water to complete their life cycle—from egg to larva to pupa, it all happens in #water. When #floods occur, all the discarded #plastic and #trash lying around fill with water and becomes the ideal breeding ground for mosquitoes.
What’s interesting is that these diseases aren’t just associated with floods—they’re also linked to #droughts. That might seem counterintuitive at first, but in many parts of the world, people don’t have safe, reliable access to clean water, especially during drought conditions. So they store water in containers that aren’t properly sealed or protected, which too can become the perfect breeding sites for mosquitoes.
Infections—particularly vector-borne diseases—are increasingly reemerging and emerging in new areas around the world for a lot of different reasons. Climate change is definitely part of that, with rising temperatures and more extreme weather events like floods and droughts. But the way we live our lives and interact with the environment also plays a huge role. I mean, first and foremost, most of us now live in urban areas rather than rural ones..."
https://insideclimatenews.org/news/26042025/climate-change-shifting-spread-of-infectious-disease/
Pathogens and treatment of a local infection
In case of local infection with such diseases such as: prostate abscess, lymphangitis, dental abscess, the causative agents of which are Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Proteus, Enterococcus, gonococcus, Escherichia coli, beta-hemolytic
streptococcus, streptococcus viridans, anaerobic staphylococci, penicillin is used, oxacillin, ampicillin, erythromycin, cephaloridine.
"Alfred says salmon populations have rebounded since most of the open-net salmon farms around the Broughton archipelago were closed two years ago."
#pathogens #salmon #BC
https://www.cbc.ca/news/canada/british-columbia/open-net-slamon-farm-pathogens-1.7512376
The #WHO #Bacterial Priority #Pathogens #List 2024: a prioritisation study to guide research, development, and public health strategies against antimicrobial resistance, https://etidiohnew.blogspot.com/2025/04/the-who-bacterial-priority-pathogens.html
#RNA interference is an important tool to protect #plants from #pathogens and pests, but delivery can be problematic. In this #JIPB review, Xing et al. explore the potential of engineered #nanotransporters for RNAi delivery.
https://doi.org/10.1111/jipb.13887
@wileyplantsci
#PlantSci #RNAi #Nanotech #botany
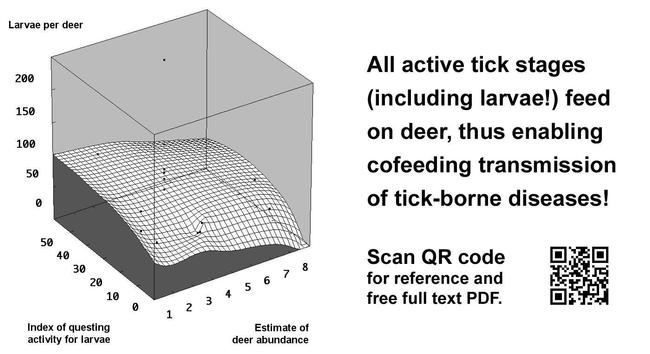
All #active #tick #stages (including #Larvae !) feed on #deer , thus enabling #cofeeding #transmission of tick-borne #Diseases
#FREE #Full #text #PDF available at https://goo.gl/gEAbfN
#Ixodes #ricinus #Capreolus #capreolus
#EU #FP6 #EDEN #Project #Emerging #Diseases in a changing #European #eNvironment #Epidemiology #Ticks #Parasites #Pathogens #Science #Scientific #Research #Data #OpenAccess #DOI #Germany #Deutschland #Europe #Europa #TBD #Zoonoses #ZoonoticDiseases #TickBorneDiseases
Rates of #infection with other #pathogens after a positive #COVID19 test versus a negative test in #US #veterans (November, 2021, to December, 2023): a retrospective cohort study, https://etidiohnew.blogspot.com/2025/04/rates-of-infection-with-other-pathogens.html
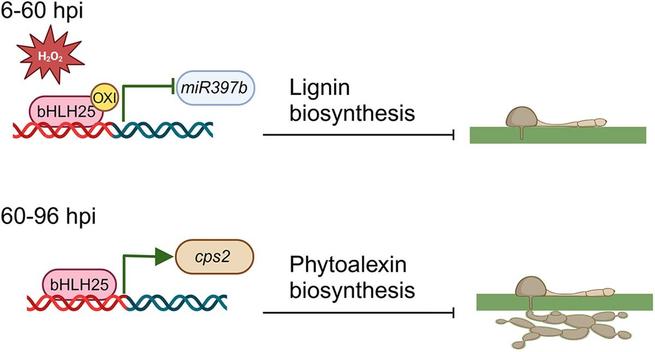
Transcription factor bHLH25 plays a dual role in #plant defense.
🛡️Oxidized, it boosts #lignin production to strengthen #cell walls against #pathogens.
⚔️Non-oxidized, it activates #phytoalexins to inhibit pathogen growth.
🤝Together, these functions may help us create disease-resistant #crops without yield loss.
🔓👇
https://doi.org/10.1111/jipb.13878
@wileyplantsci
#PlantSci #JIPB #botany
New #antibiotic that kills #drugresistant #bacteria discovered in technician’s #garden
It targets bacteria’s protein-making factory, the #ribosome, in a way that other antibiotic drugs don’t. Ribosome is an attractive antibiotic target because bacteria don’t easily develop resistance to #drugs targeting the structure. In studies, #lariocidin slowed the growth of a range of common bacterial #pathogens, including many multidrug-resistant strains.
https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-025-00945-z
https://archive.ph/NHtJh
H.H.S. Scraps Studies of #Vaccines and Treatments for Future #Pandemics
Federal officials cited the end of the Covid-19 #pandemic in halting the research. But much of the work was focused on preventing outbreaks of other #pathogens.
#COVID19 #medicine #hhs #rfkjr
https://www.nytimes.com/2025/03/26/health/future-pandemics-vaccines-funding.html
The #epidemiology of #pathogens with #pandemic potential: A review of key parameters and clustering analysis, https://etidiohnew.blogspot.com/2025/03/the-epidemiology-of-pathogens-with.html
🤗🤗🤗 We welcome Fabian Royer as PhD student @Mol_Ecol @uniinnsbruck !
Fabian will work on the #ConservationBiology of wild #bees in Central Europe.
Deadly #mold strains highly likely to acquire #resistance to new #drugs.
#evolve_not_acquire #fungus #pathogens #fungicides #ipflufenoquin #Aspergillus #mutation #selection
https://phys.org/news/2024-12-deadly-mold-strains-highly-resistance.html